In today’s data-driven world, businesses need systems that can handle massive amounts of data while remaining flexible and easy to use. Microsoft Fabric’s Lakehouse combines the best of data lakes and data warehouses into a single, unified platform. Whether you’re a data professional or a curious learner, this guide will walk you through creating and managing a Lakehouse in Microsoft Fabric—even if you’re new to the concept.
Table of Contents
- What is a Lakehouse?
- Why Microsoft Fabric for Your Lakehouse?
- Step-by-step guide:
- Tips for Success
- Conclusion
What is a Lakehouse?
Before diving into the “how,” let’s understand the “what.”
A Lakehouse is a modern data architecture that blends the flexibility of data lakes with the structured, query-optimized nature of data warehouses. Think of it as:
- A data lake: It stores raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data like JSON, CSV, and Parquet files.
- A data warehouse: It organizes data into tables for easy querying, enabling analytics and reporting.
With a Lakehouse, you don’t have to move data between systems for different purposes—it’s all handled in one place.
Why Microsoft Fabric for Your Lakehouse?
Microsoft Fabric elevates the Lakehouse concept with:
- OneLake: A unified data storage solution, allowing you to centralize data.
- Delta Lake: Provides features like ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability) transactions, time travel, and scalability.
- Built-in Integration: Seamless connection to Power BI, Azure Synapse, and real-time analytics tools.
Step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Setting Up Your Workspace
If you do not already have a Workspace you first need to create one. The Workspace will act as the home for your Lakehouse.
- Log in to Microsoft Fabric: Access the platform through your organization’s Microsoft account.
- Create a New Workspace: In the portal, navigate to Workspaces > Create New Workspace, give it a name (e.g., “Analytics Lab”), and set permissions.
Step 2: Creating the Lakehouse
Once your workspace is ready, create your Lakehouse:
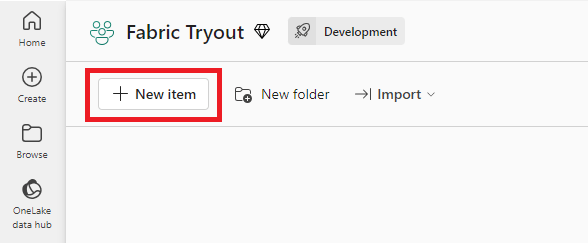
- Go to New item > Lakehouse within your workspace.

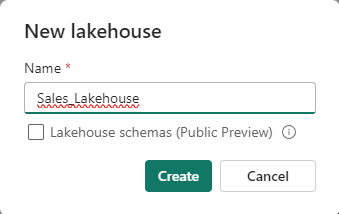
2. Name your Lakehouse (e.g., “Sales_Lakehouse”) and click Create.
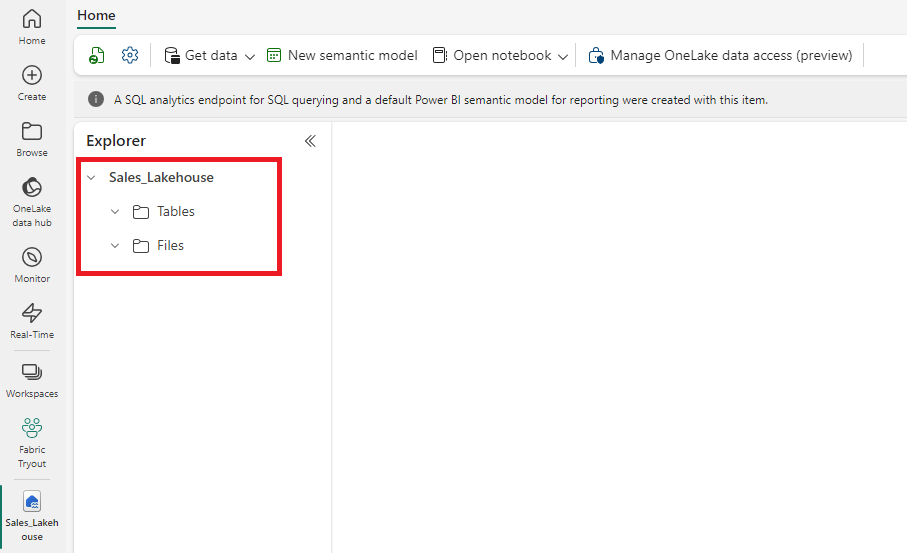
3. Explore the Lakehouse structure:
- Files: For raw data uploads (e.g., CSV, JSON, Parquet).
- Tables: For structured, queryable data.
Step 3: Adding Data to the Lakehouse
A Lakehouse without data is like a library without books. Here’s how to populate it:
- Upload Data Files:
- Drag and drop files into the Files area.
- Alternatively, use the Ingest Data tool for bulk uploads.
- Automate Data Ingestion:
- Connect to external sources like SQL databases, APIs, or other data lakes using Pipelines.
- Set up recurring ingestion schedules for automated updates.
- Real-Time Data Streaming:
- Stream real-time data from IoT devices or platforms like Apache Kafka or Azure IoT EventHub.
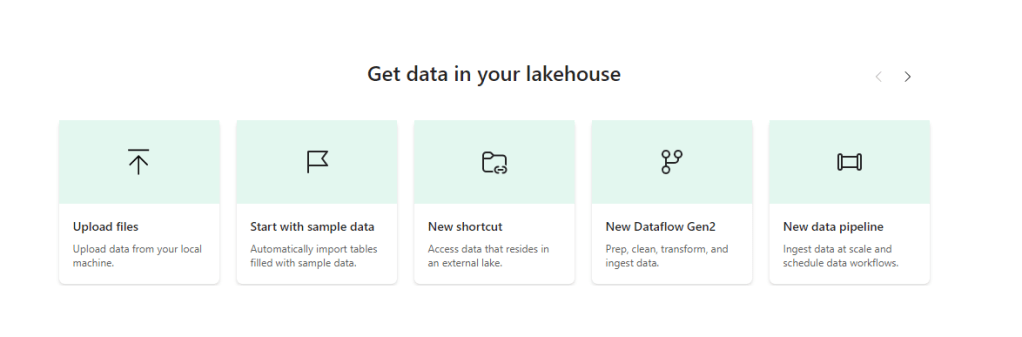
In this example we are going to use the sample data.
Step 4: Organizing Data into Tables
Raw data is powerful but often hard to work with. Tables transform that raw data into a usable format.
- Right-click a file in the Files area and choose Load to Tables > New table.
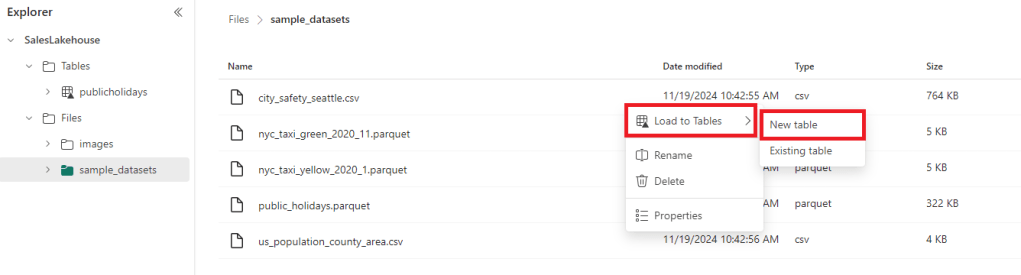
2. Define how the data should be loaded into the new table. In this case we use the headers in the files as column names and the comma (,) as the separator. To know what settings to choose it is useful to have a look at the raw files.
Step 5: Analyzing and Visualizing Data
Microsoft Fabric makes data analysis straightforward:
- Query Tables with SQL:
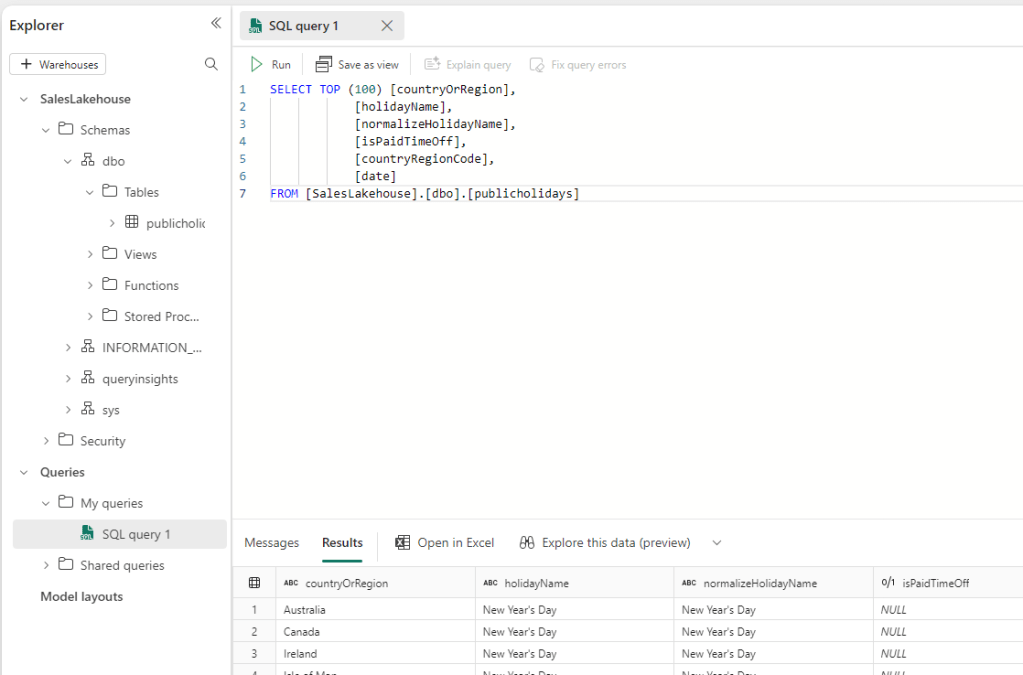
- Each Lakehouse comes with an SQL Endpoint. Using this Endpoint you can run your queries directly against the Lakehouse tables.
2. Build Dashboards in Power BI:
- Connect your Lakehouse to Power BI for real-time analytics and reporting.
- Use Direct Lake mode to minimize latency.
3. Explore with Notebooks:
- Write Python or Spark scripts to perform advanced analytics and machine learning.
- Share notebooks with team members for collaboration.
Tips for Success
- Plan Your Architecture: Think about how you’ll organize data—by department, region, or project for example.
- Stay Updated: Microsoft regularly releases updates, so keep an eye out for new features.
Conclusion
Microsoft Fabric’s Lakehouse is a powerful tool that simplifies data storage, analysis, and governance. Whether you’re working with structured business data or unstructured logs, Fabric’s Lakehouse ensures you can manage it all in one place.